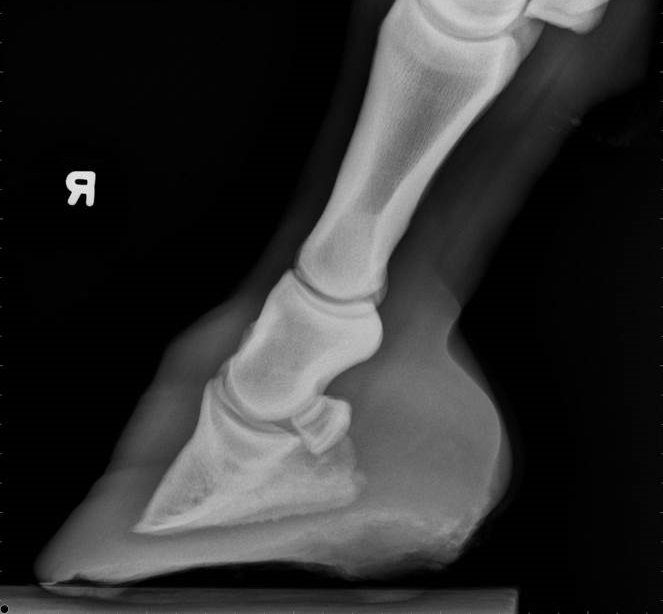
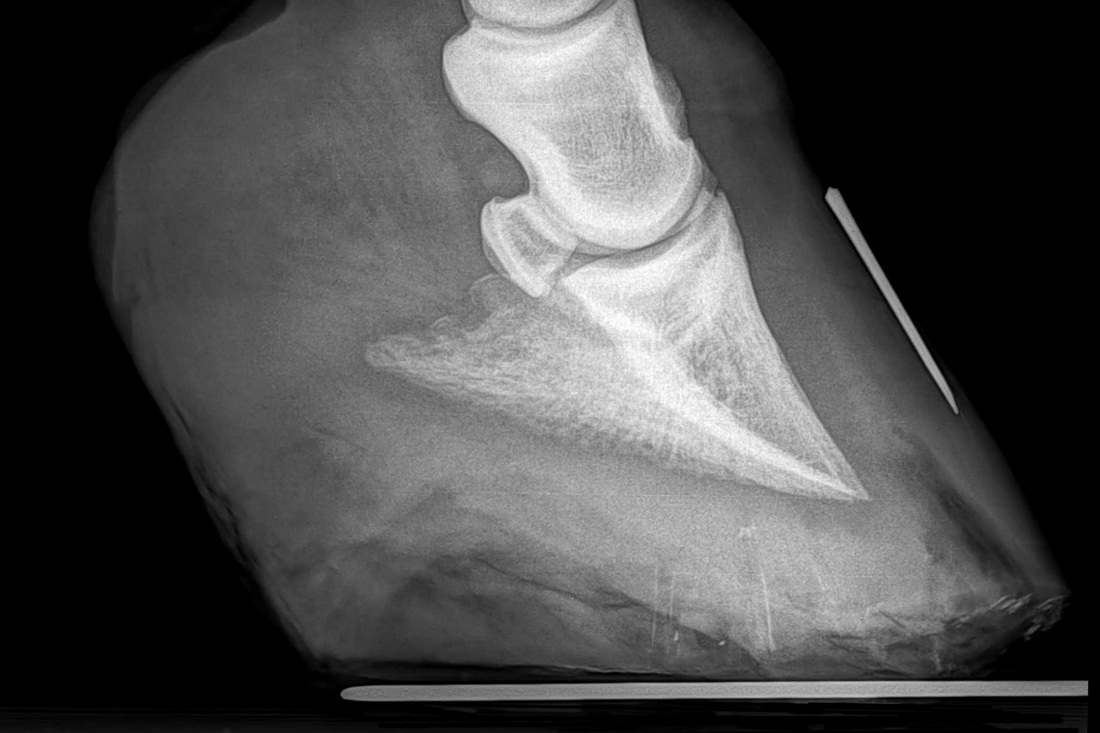
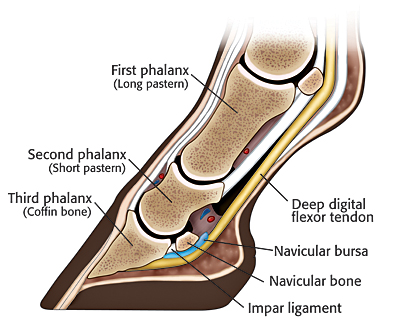
Radiographs, commonly known as xrays, are often taken during lameness exams to visualise the bones and joints Portable digital systems (DR) are mostly used for lower limb examinations and are especially useful if it is difficult or unsafe to travel an injured horse If your vet feels that xrays of the upper limbs, spine or thorax are neededThe name of the view describes the direction of the xray beam The beam is aimed from dorsoproximal to palmarodistal at a 65 degree angle to the sole of the foot This view may be obtained with the horse standing on the cassette as in this illustration The xray beam is centered at the coronary band Notice in the photo that the cassette The xrays showed fractures in the lateral cartilage (or sidebones) on both front feet The vet said these fractures were due to the extreme pressure put on the cartilage (due to the size and placementof the sidebone) and also the lack of shock absorption (due to heel contraction and size of the hoof)
Http Www Horseandriderbooks Com Pdfs Essential hoof Excerpt Pdf
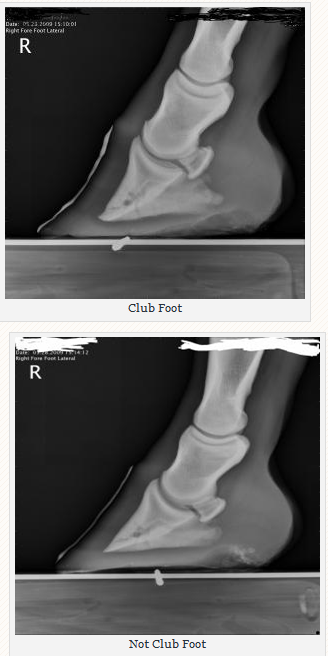
Club foot horse x ray
Club foot horse x ray-From the case Talipes equinovarus (clubfoot) Xray Lateral Lateral radiograph of the right foot shows that the long axes of the talus and calcaneus are nearly parallel The longitudinal arch is abnormally high AP radiograph of the right foot shows abnormally narrow talocalcaneal angle, with severe adduction and supination of the forefootThe xray will show whether the hoof pastern axis is parallel If the axis is broken forward (club foot) or if the axis is broken back (long toe underrun heel), the radiograph will reveal the degree of deformity and the best way to trim the foot to improve it Using landmarks, measurements can be drawn on the radiographs and transferred to the foot




Radiography Of The Equine Stifle Part 4 Of 4 Imv Imaging
Lisfranc injury The 'Lisfranc' ligament stabilises the midforefoot junction Loss of alignment of the 2nd metatarsal base with the intermediate cuneiform indicates injury to this important ligament Every posttraumatic foot Xray must be checked for loss of alignment at the midfootforefoot junction (tarsometatarsal joints)F351 76s 13~ of lb florida state racing commission /o/b, honorable charley e johns acting governor of florida for the fiscal year ending june 30, 1954 ray eClub foot refers to a limb flaw, where the hoof is very upright with a long heel This is the most common tendon flaw in foals The deep digital flexor tendon (DDFT) is much shorter than the bones Thus, it pulls on and rotates the coffin bone downward in the hoof In general, club foot most commonly occurs in the front legs
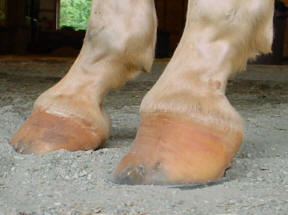
An X ray of your horse's footcan help you predict thefuture while it shows youthe present Physical examination remains the most important part of examining the foot, says Redden, followed bytargeted radiographs Congential Talipes equinovarus it`s a common form of clubfoot Talipes = talus (ankle) pes (foot) Equino = heel is elevated (like a horse's) varus = turned inward With this type of clubfoot, the foot is turned in sharply and the person seems to be walkingon their ankle 3 Club Feet Prevention, Treatment & Correction Anyone who has spent any time with equines has undoubtedly seen club feet A club foot horse is typically recognized and defined as having one front hoof growing at a much steeper angle than the other, with a short dished toe, very high heels, extremely curved wall and straight bars The club foot is also generally much
With his work in Kentucky, Craig Lesser finds management of club feet to be a common issue Practicing out of Rood & Riddle Equine Hospital in Lexington, Ky, the equine veterinarian and American Farrier's Association certified farrier approaches these cases from that dual perspective He presented on the subject at the 18 American Association of Equine Practitioners Congenital talipes equinovarus (club foot/ctev) ppt by Dr Pratik Download Now Download Download to read offline Health & Medicine Jun 27, 18 33,762 views ctev (club foot) with its aetiology, pathological anatomy, classification, When asked to work on a horse with a club foot, take extra time to evaluate the whole horse Look at the horse from all angles Watch the horse as it takes a couple of steps;



Hoof Care For The Club Footed Horse David Farmilo




Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site
The same horse's radiographs give the same information Fig 7 and 9 were taken a year before I first saw the horse and the photo above was taken It appears the sole was a bit thicker, rotation less and distal descent less severe at that time, than what IPositioning the foot for the examination Blocks are needed to elevate the off the ground allowing the foot to be centered in the cassette and the xray beam to pass horizontally through the specific area of interest (ie solar surface of the foot, DIP joint, navicular, etc) A club foot alters a horse's hoof biomechanics, frequently leading to secondary lamenesses Affected horses tend to land toefirst, and their heel's growth rate is




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome



1
"If you have a broad rule or method that you apply to all horses, it may work on some but it won't work on others You need to be open to many methods, and creative, and try to understand what caused this club foot Having xrays can be helpful, to determine sole thickness and the shape of the coffin bone and whether there is any rotationRadiographs (xray pictures) may reveal damage to the navicular bone but bone changes can be difficult to interpret, as there are differing opinions on what is 'normal' Navicular syndrome can exist without demonstrable radiographic abnormality and magnetic resonance imagining (MRI) may reveal injury to the impar or other ligaments or soft tissues A horse with a club foot is kind of like a horse in high heels The hoof angle becomes raised and the horse walks on his toe due to a shortening of the musculotendinous unit (the unit including



So Called Club Foot By James R Rooney Dmv




Laminitis An Overview Essential Reading Everything Horse
This can help you see where the foot cannot take stress Photo 9 is the lateral xray showing the remodeled bone and poor quality of the boneMichael H Wilensky M D Lllp General Orthopedic Clinic Biscayne Blvd, Suite 108, Aventura, FL Club Foot Horses Versus Uneven Weight Distribution First off let's discuss exactly what a "club foot" is This term is widely misused with regard to its use in horses with uneven hoof growth patterns The term "club foot" actually refers to a congenital defect of the foot and according to The Free Dictionary,




Radiography Of The Equine Stifle Part 4 Of 4 Imv Imaging



Www Theneaep Com S Xia1nkm5hdp7yhwyucxfn39k42qa8m
The equine club foot is defined as a hoof angle greater than 60 degrees What we see externally as the equine clubbed foot is actually caused by a flexural deformity of the distal interphalangeal joint (coffin joint) Causes include nutritional issues, heredity, position in the uterus or injury The condition is most often encountered in young animals and can be either congenital (they are bornExplore LISA's board "equine clubfoot" on See more ideas about horse health, equines, horse care tipsXRay Exam Foot What It Is A foot Xray is a safe and painless test that uses a small amount of radiation to make an image of a person's foot During the examination, an Xray machine sends a beam of radiation through the foot, and an image is recorded on special Xray film or a computer



ep Org Sites Default Files Issues Proceedings 12proceedings In Depth The Foot From Every Angle Eggleston Pdf




Why Is My Horse So Hairy Prescott Animal Hospital Equine Center
Start Early Redden says a grade 1 or 2 club foot is often found in foals as young as 1 month, although it is normally 4 or 5 months before a noticeable problem is detected "Newborn foals that have a significant deep flexor contraction are often up on their toes or even knuckled over with the more severe contraction," Talocalcaneal parallelism is the radiographic feature of clubfoot (talipes) Simulated weightbearing xrays are used for infants who have not commenced walking Positioning for foot xrays is very important The anteroposterior (AP) view is taken with the foot in 30° of plantarflexion and the tube at 30° from vertical Find foot xray stock images in HD and millions of other royaltyfree stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the collection Thousands of new, highquality pictures added every day




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Barehoofcare Com Wp Wp Content Uploads 15 07 Club Foot Pdf
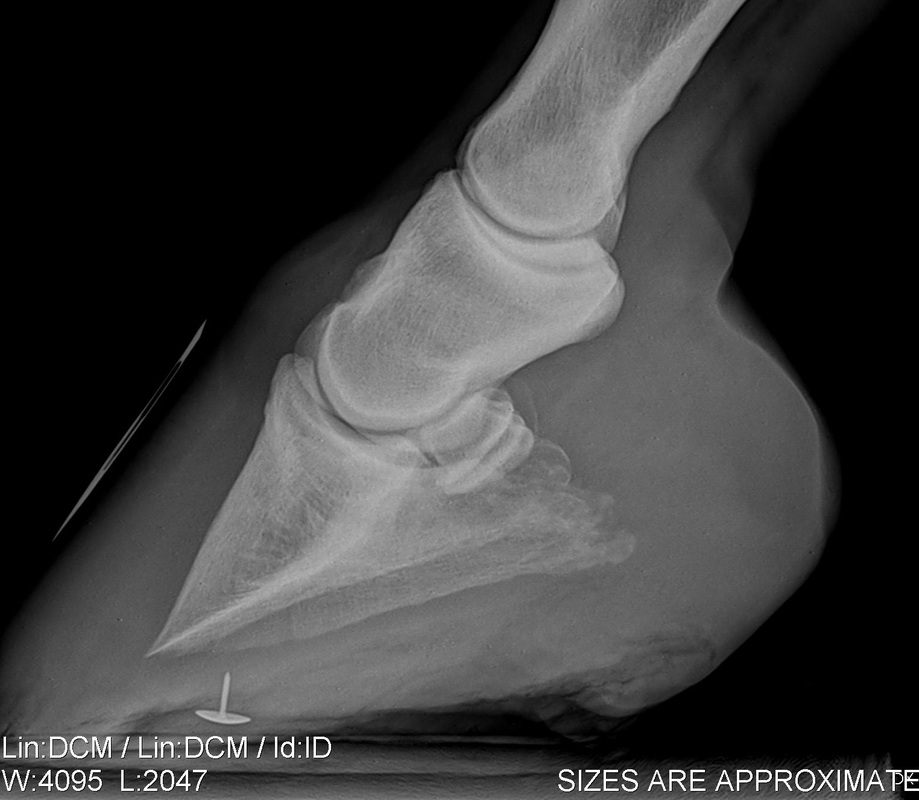
Sette and the xray beam is angled between 35° and 45° to the cassette This projection will show the posterior subtalar joint laterally and the sustentacular facet medially Therefore, this view can reveal coalition between the sustentaculum and the talus at the middle facet, and less commonly, coalition in the posterior facetIn the club foot because the deep flexor tendon is contracted, the xray will show that the pedal bone angles are quite different, the front is not in line with the hoof wall, the tip is pointing down and the rear part is much greater than five degrees Put simply, the heels will need to be lowered and any flare corrected at the toe The contracted muscle/club foot condition is a common growth problem in young horses (up to 6 months of age), causing upright pasterns and a tiptoe stance This is often seen in foals with developmental problems due to rapid growth If discovered soon enough, this condition can be reversed by altering the foal's diet and reducing stress on



Managing The Club Hoof Easycare Hoof Boot News




Progressive Equine Services Hoof Care Centre Home Facebook
Waldsmith noted that there are various ways to digitally image a horse, but that "The biggest difference is the variability of the Xray dose," he said "This is dependent on the Xray machine's capability, and also age Many times as Xray generators age the Xray dose that is actually produced is less than what the settings indicate" The image on the left represents what is happening in a horse with a club foot, where the excess tension from the deep digital flexor tendon pulling on the back of the coffin bone is essentially holding the heel off the ground, preventing the horse from fully loading its heel Understanding hoof Xrays Horse & Hound 31 July, 06 1237 Diagnostic techniques For many years, Xrays have been the major imaging technique for evaluation of the foot, for both diagnosis and



Podiatry Burwash Equine Services



Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles
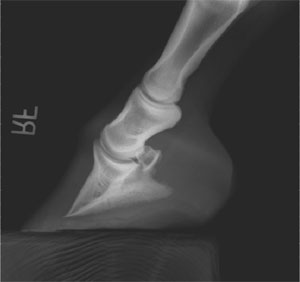
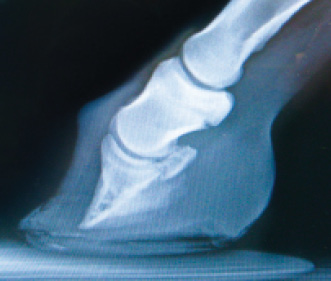
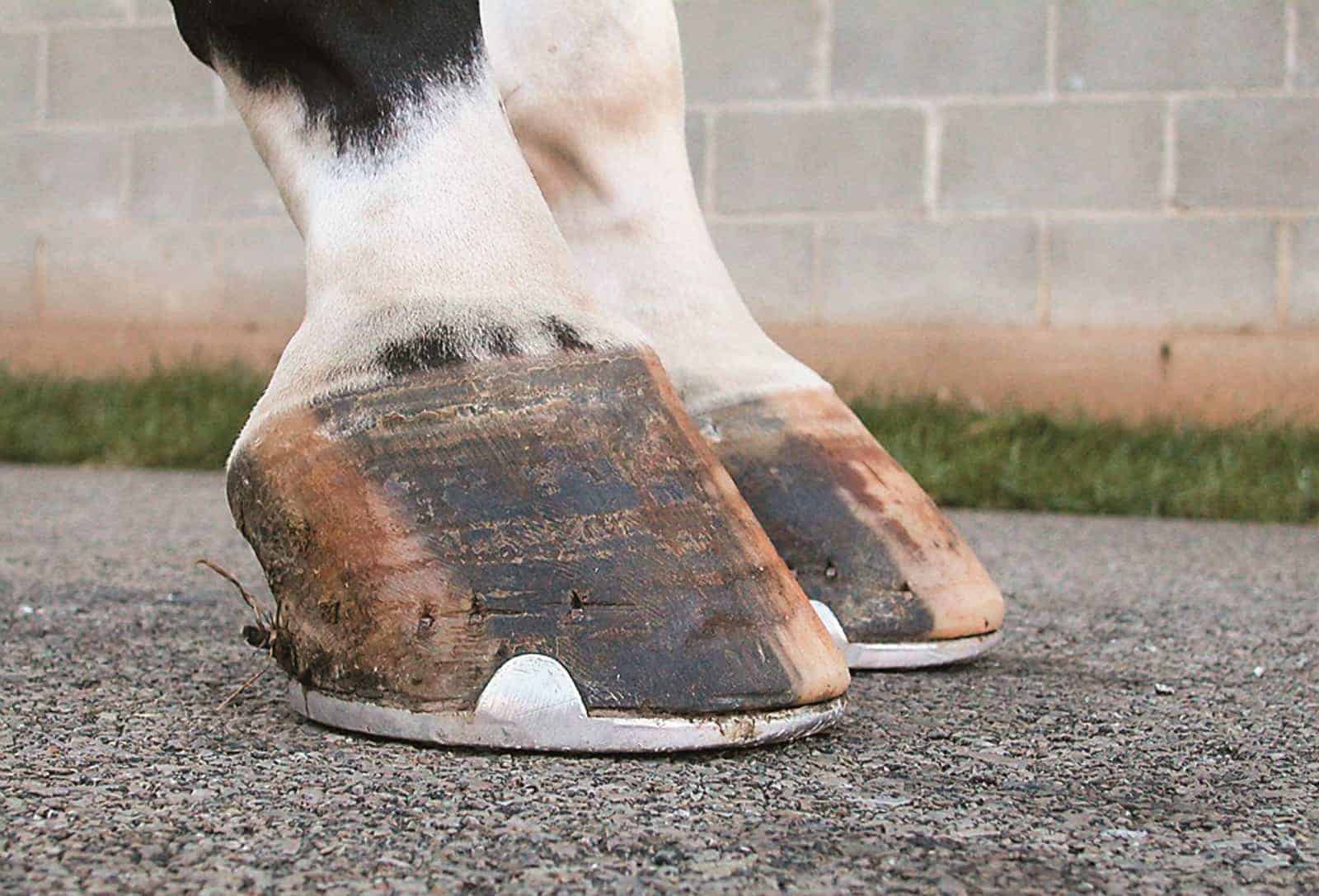
Horse with club foot has one hoof that grows more upright than the other The "up" foot is accompanied by a broken forward pastern, that is, the hoof is steeper than the pastern (Photo 1) In a normal foot, the hoof capsule and the pastern align Radiographs will show that the boney column itself is misaligned, with permanent rotation of the coffin joint (Photos 2 and 3)The beam orientation is parallel to the dorsalpalmar/plantar long axis of the foot on the median plane of the foot For consistency, the xray beam is also centered 15 to 2 cm above the weight bearing surface of the foot Caused by abnormal contraction of the deep digital flexor tendon, a club foot puts pressure on the coffin joint and initiates a change in a hoof's biomechanics Telltale signs of a club foot may include an excessively steep hoof angle, a distended coronary band, growth rings that are wider at the heels, contracted heels, and dished toes Most horses only have one club foot, but it




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Farrier Terms Decoded Top 5 Farriery Terms Horse Owners Should Know Badger Veterinary Hospital
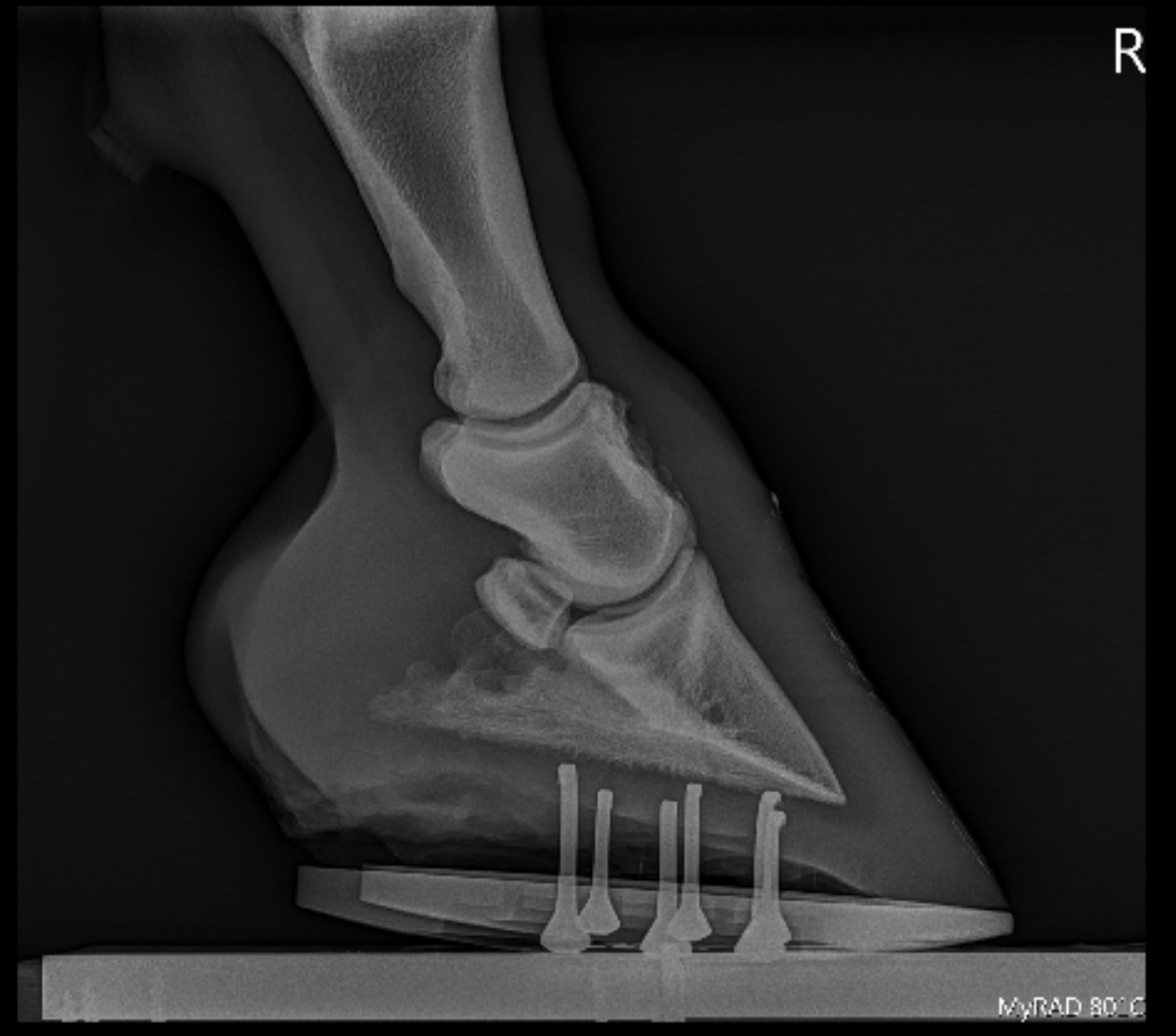
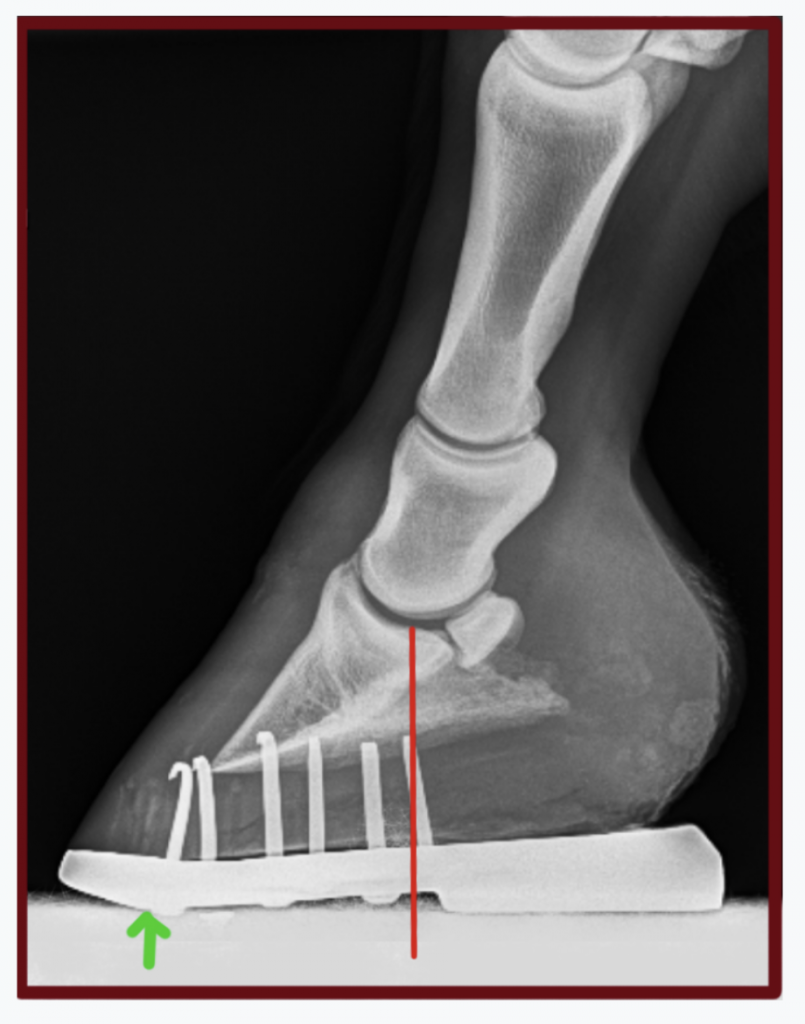
Xrays (correctly called radiographs) are essential for assessing changes in the feet following laminitis, and should clearly show the relationship between the hoof capsule and the internal structures of the foot to help the hoofcare professional Correctly marked and positioned xrays can be used to assess the severity of changes/damage, reach a prognosis, and monitor response toXray of feet (typical clubfoot) Clubfoot Introduction Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus – TEV) is one of the major orthopedic conditions of childhood One of the most common of all birth defects, clubfoot affects about 1 in 400 babies born in the United States each year Boys are affected twice as often as girls Causes The exact cause of clubfoot remains unclear Characteristics of xray machines essential to perform foot examinations on a horse are (1) the tube has to be able to project in a horizontal direction from the floor or ground surface, (2) the tube head must be easily angulated to form different angles between horizontal and vertical, and (3) the xray machine must be easily and quietly



Epublishing




Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site
The xray beam should be directed horizontally, centered on the femorotibial joint, caudal and distal to the apex of the patella The beam will most commonly be directed 10° to ° caudal to cranial to the frontal plane to accommodate for the typical hind limb anatomy of most horses As a rule of thumb, align the beam parallel to the heelWritten and presented April 12 by RF (Ric) Redden, DVM To better understand the club foot syndrome, we must be familiar with the mechanical formula and how it greatly influences the various degrees of hoof capsule distortion and bone remodeling associated with this syndrome There appears to be a direct relationship between the degree of tension increase or contributiveVideo Club Foot in Horses In this excerpt from the November 18 episode of Ask the Vet, Dr Gray and SmartPaker Dan turn to Danvers Child, the SmartPak Hoof Health Consultant, for assistance with a question on a horse with a club foot to clear up some confusion around the topic




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses



Http Www Horseandriderbooks Com Pdfs Essential hoof Excerpt Pdf
Any club foot that has been around a while will have a sensitive, unused, underdeveloped frog/digital cushion You can fix everything else and still have the back of the foot too sensitive for the horse to land on, which will cause the shortened stride and resulting club foot on its own – another vicious cycleSymptoms of Club Foot in Horses Lameness Pain Excess toe wear Shortening of the tendon that is attached to the coffin bone Impacts the standing or movement of your young horse It can affect one or both limbs usually in the fore limbs Coronary band may bulge as the deformity progressesRadiographs may show chronic changes to the coffin bone from excessive concussion, and excessive pull from the deep flexor tendon In most cases of adult club foot, it is not possible to simply shorten the heel to create a normal conformation The problem with club foot is abnormal forces generated in the hoof




Managing The Club Foot The Horse



Sports Medicine And Lameness Palmetto Equine Veterinary Services




Radiography Techniques Of The Equine Fetlock Joint Imv Imaging



Club Foot




The Wild Mustang Hoof



Understanding Navicular Syndrome Heel Pain In Horses



Q Tbn And9gct650ae6d8vnmqnvcvl4zcvlmqyfuvklxwislafu3ckq06siyee Usqp Cau




The Wild Mustang Hoof



1




Clubfoot Barefoot Hoofcare




Shoeing Options For Club Foot In Horses



Equine Podiatry Say What Mobile Veterinary Services




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource




Severe Lameness Scarsdale Vets




Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome



Barehoofcare Com Wp Wp Content Uploads 15 07 Club Foot Pdf




Laminitis A Pictorial Review



Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site



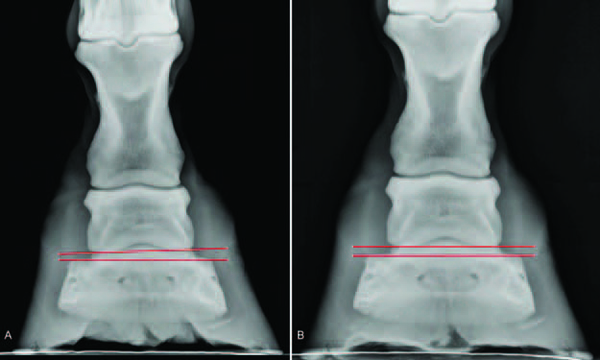
Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site



Thrush Cured Cowboy Pads And Copper Sulfate




Hoof Evaluation Radiographs For The Farrier




Hoof Evaluation Radiographs For The Farrier




Radiolucency Glue On Horseshoes By Sound Horse Technologies




Foal With Hoof Problems Club Foot The Horse



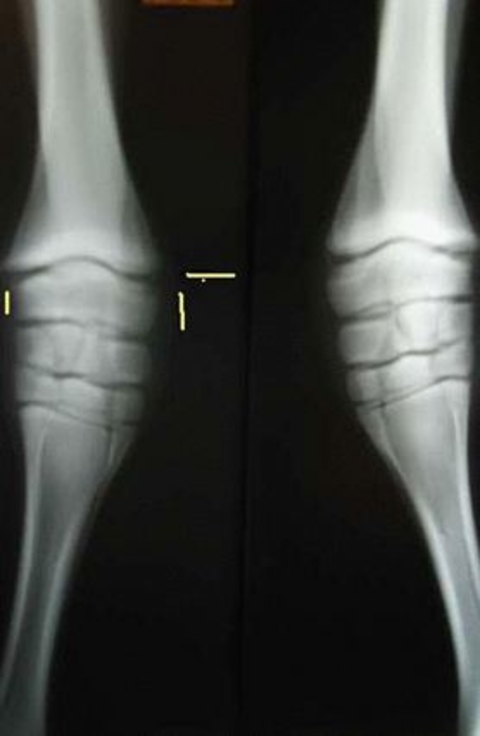
Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles



Types Of Crooked Legs In Foals




The Progressive Equine Services Hoof Care Centre Facebook




Does My Horse Have Pyramidal Hoof Disease The Horse




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Equine Podiatry Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles



Boarding At Yucca Veterinary Medical Center



Low Foot Case Study Dixie S Farrier Service




Hoof Conformation Vs Horse Conformation Scoot Boots Us Retail




Fighting Laminitis Expert How To For English Riders
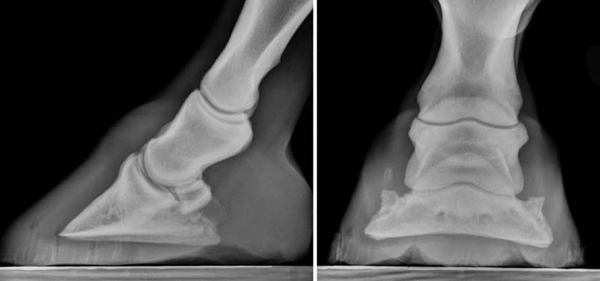



Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles




Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles American Farriers Journal




Filly With Club Foot Barefoot Hoofcare




Club Foot Or Not Barefoot Hoofcare




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Www Theneaep Com S Xia1nkm5hdp7yhwyucxfn39k42qa8m




Michael Porter Equine Veterinarian 12




The Importance Of Physical Maturity In The Horse Horsetalk Co Nz



Viewing A Thread Ringbone Help



Club And Subluxation In The Proximal Interfalangian Articulation Farriers Forum




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals



Www Theneaep Com S Xia1nkm5hdp7yhwyucxfn39k42qa8m



ep Org Sites Default Files Issues Proceedings 12proceedings In Depth The Foot From Every Angle Eggleston Pdf




Club Feet On X Ray Youtube



The Chronicle Of The Horse



Performanceequinevs Com Wp Content Uploads 19 12 Equine Foot Secrets Ebook Compressed Pdf



ep Org Sites Default Files Issues Proceedings 12proceedings In Depth The Foot From Every Angle Eggleston Pdf




Farriery For The Hoof With A High Heel Or Club Foot Semantic Scholar




Hoof Evaluation Radiographs For The Farrier




How To Treat Club Feet And Closely Related Deep Flexor Contraction



Clubfoot Imaging Practice Essentials Radiography Computed Tomography



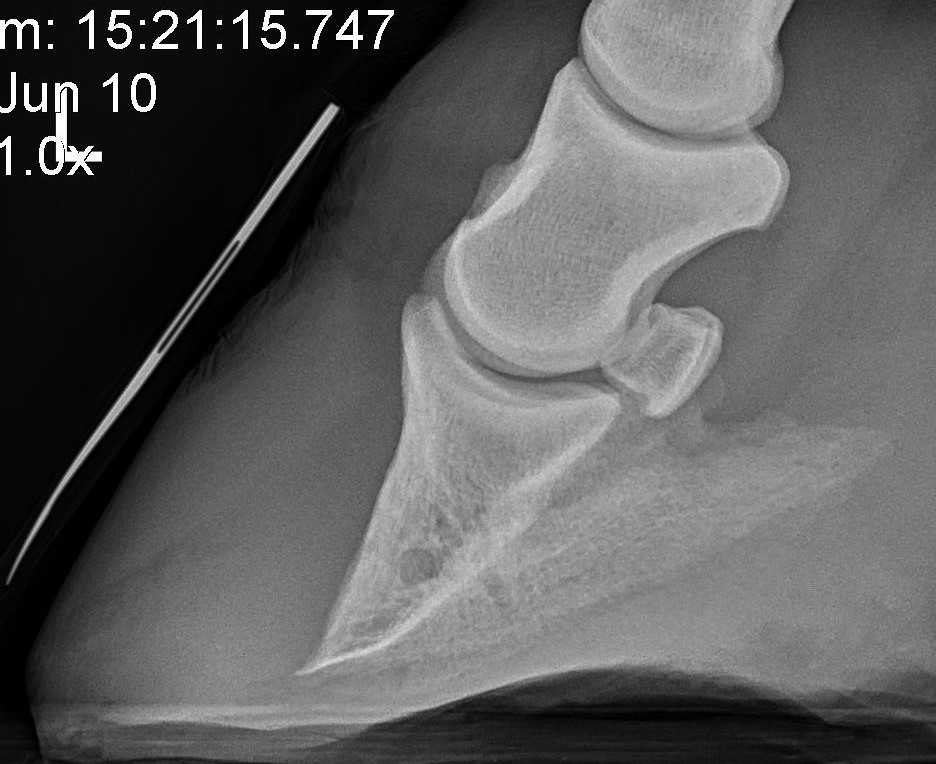
Understanding Navicular Syndrome Heel Pain In Horses




Pro Equine Grooms Contracted Heels In Horses



1




Fighting Laminitis Expert How To For English Riders




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




Natural Angle Volume 15 Issue 1 Spanish Lake Blacksmith



Basic Shoeing Working With A Club Foot Farrier Product Distribution Blog



Low Foot Case Study Dixie S Farrier Service




Horseadvice Com Equine Horse Advice 22 Months Old With A Club Foot



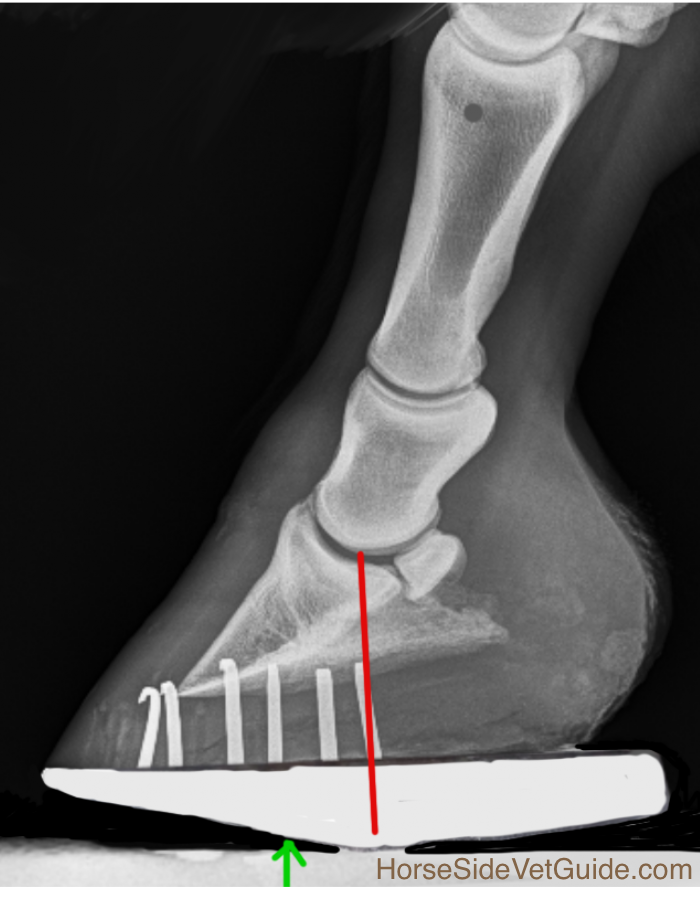
Why I Recommend Every Laminitis Case Has X Rays Riding Equine Vets
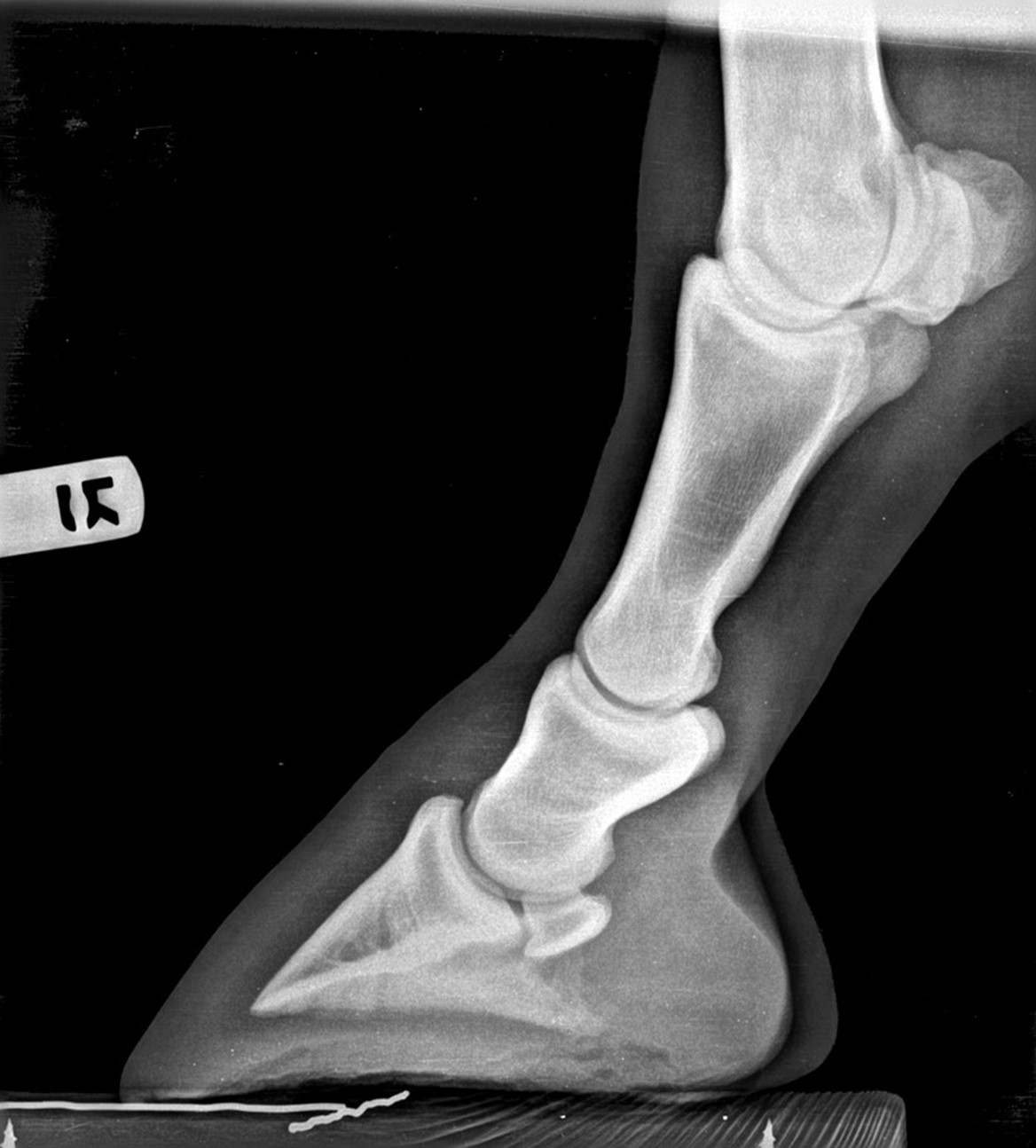



Hoof Radiographs Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic




Rear Hoof Imbalance And The Effect On Rearlimb Lameness




Recognizing And Managing The Club Foot In Horses Horse Journals




Laminitis A Pictorial Review




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource
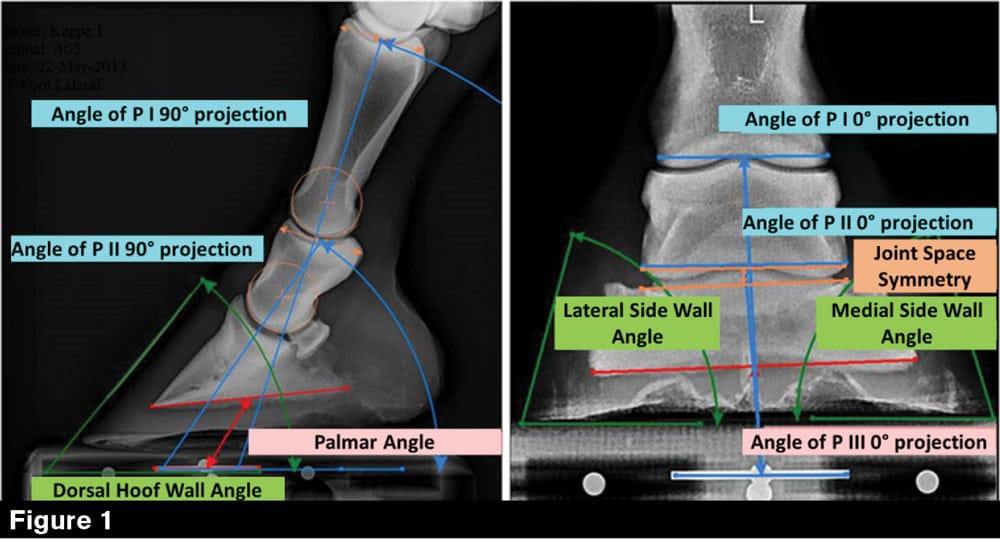



Effects Of Trimming On Shape And Dimensions Of The Hoof Capsule As Well As On The Phalangeal Alignment American Farriers Journal




Club Foot In Horses Brian S Burks Fox Run Equine Center Facebook
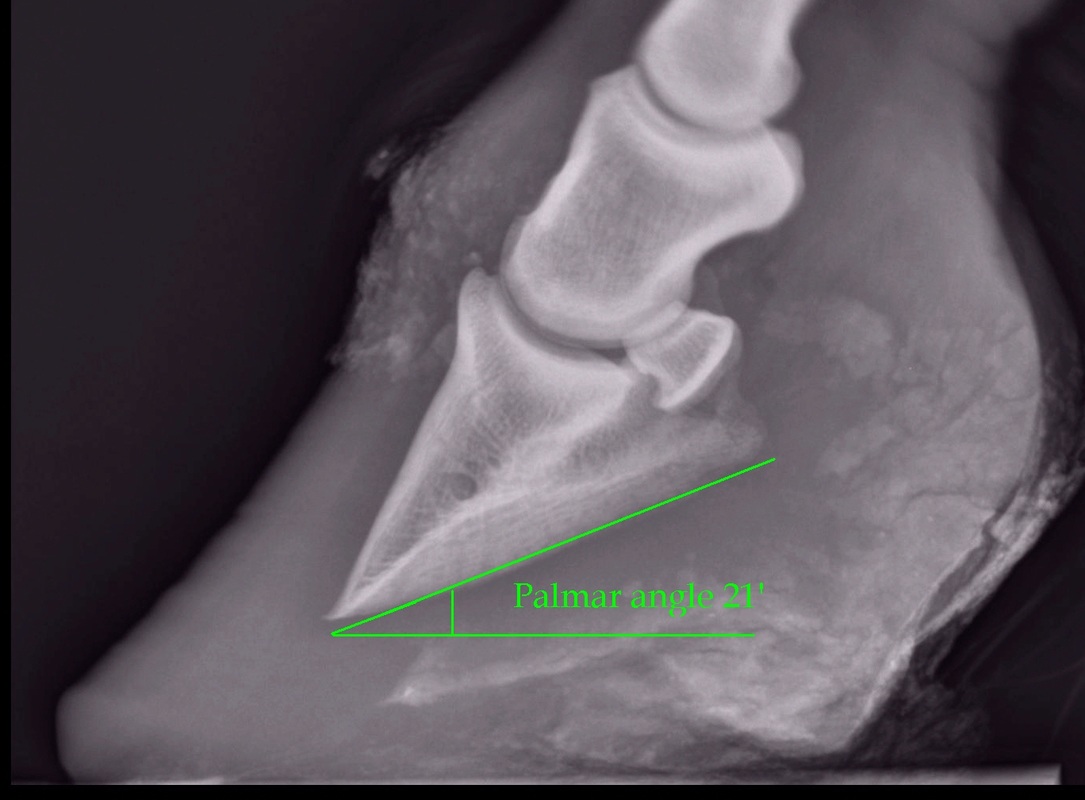



Understanding X Rays The Laminitis Site
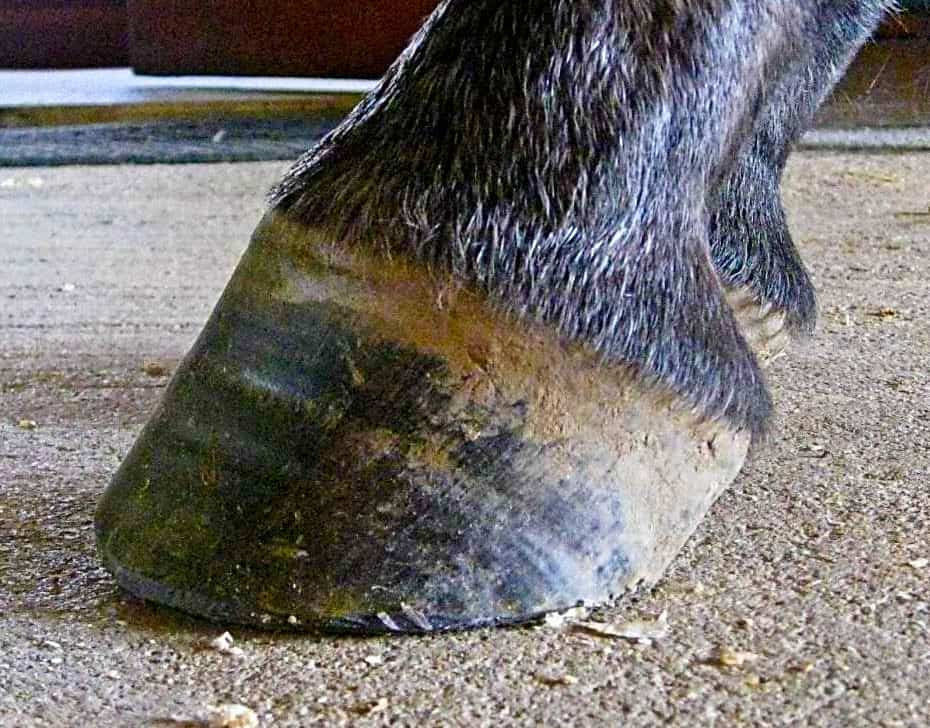



Hot Topics In Hoof Care Part 4 The Abnormal Horse Hoof The Horse
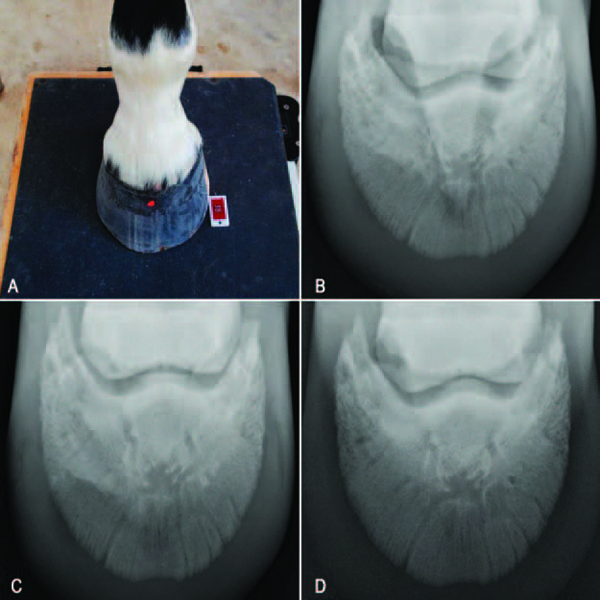



Equine Therapeutic Farriery Dr Stephen O Grady Veterinarians Farriers Books Articles




Understanding Club Foot The Horse Owner S Resource




The Truth About Hoof Pastern Axis



ep Org Sites Default Files Issues Proceedings 12proceedings In Depth The Foot From Every Angle Eggleston Pdf



Hoof Deformities Round Pen Square Horse
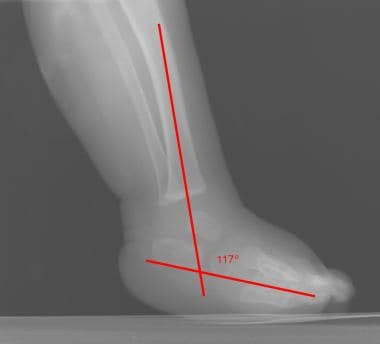



Clubfoot Imaging Practice Essentials Radiography Computed Tomography
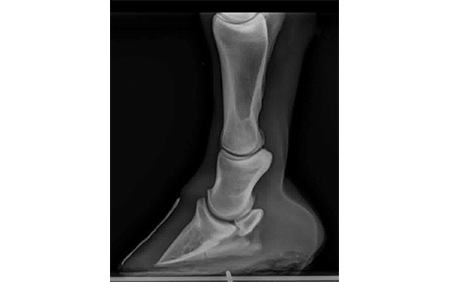



Equine Laminitis Soft Ride Boots For Equine Laminitis Comfort
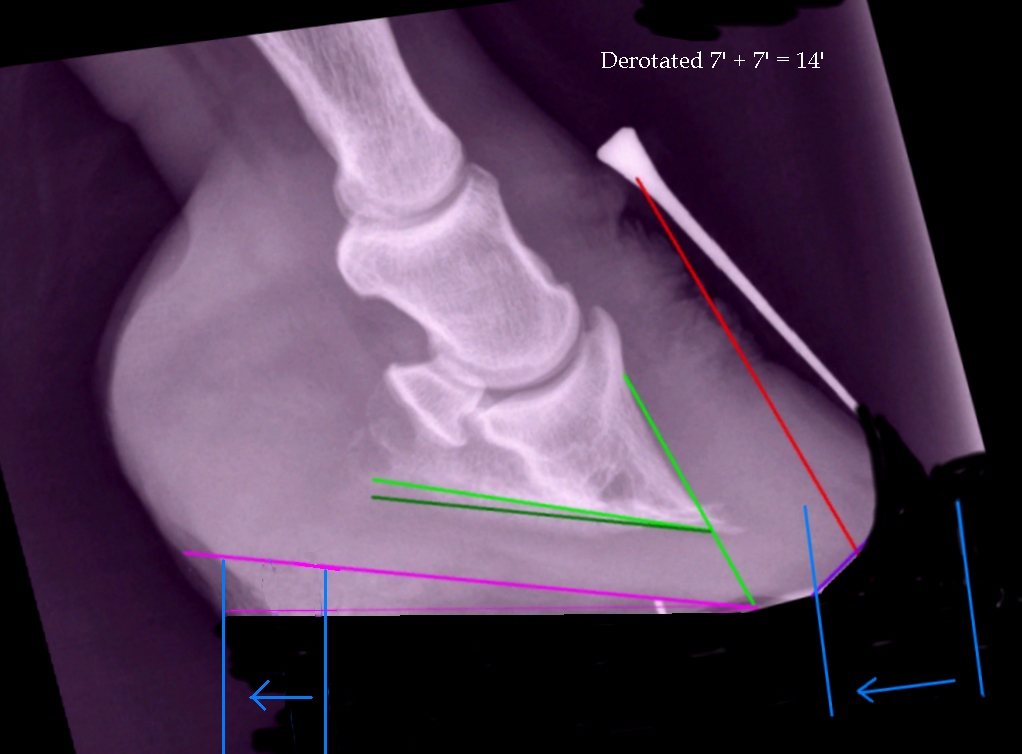



High Heels The Laminitis Site



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿